Portal:World
The World Portal

The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique, while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object, while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts.
In scientific cosmology, the world or universe is commonly defined as "the totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon, or the "horizon of all horizons". In philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind.
Theology conceptualizes the world in relation to God, for example, as God's creation, as identical to God, or as the two being interdependent. In religions, there is a tendency to downgrade the material or sensory world in favor of a spiritual world to be sought through religious practice. A comprehensive representation of the world and our place in it, as is found in religions, is known as a worldview. Cosmogony is the field that studies the origin or creation of the world, while eschatology refers to the science or doctrine of the last things or of the end of the world.
In various contexts, the term "world" takes a more restricted meaning associated, for example, with the Earth and all life on it, with humanity as a whole, or with an international or intercontinental scope. In this sense, world history refers to the history of humanity as a whole, and world politics is the discipline of political science studying issues that transcend nations and continents. Other examples include terms such as "world religion", "world language", "world government", "world war", "world population", "world economy", or "world championship". (Full article...)
Selected articles - show another
-
Image 1

Global urbanization map showing the percentage of urbanization and the biggest global population centres per country in 2018, based on UN estimates.
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It can also mean population growth in urban areas instead of rural ones. It is predominantly the process by which towns and cities are formed and become larger as more people begin to live and work in central areas.
Although the two concepts are sometimes used interchangeably, urbanization should be distinguished from urban growth. Urbanization refers to the proportion of the total national population living in areas classified as urban, whereas urban growth strictly refers to the absolute number of people living in those areas. It is predicted that by 2050, about 64% of the developing world and 86% of the developed world will be urbanized. This is predicted to generate artificial scarcities of land, lack of drinking water, playgrounds and other essential resources for most urban dwellers. The predicted urban population growth is equivalent to approximately 3 billion urbanites by 2050, much of which will occur in Africa and Asia. Notably, the United Nations has also recently projected that nearly all global population growth from 2017 to 2030 will take place in cities, with about 1.1 billion new urbanites over the next 10 years. In the long term, urbanization is expected to significantly impact the quality of life in negative ways. (Full article...) -
Image 2Internationalism is a political principle that advocates greater political or economic cooperation among states and nations. It is associated with other political movements and ideologies, but can also reflect a doctrine, belief system, or movement in itself.
Supporters of internationalism are known as internationalists and generally believe that humans should unite across national, political, cultural, racial, or class boundaries to advance their common interests, or that governments should cooperate because their mutual long-term interests are of greater importance than their short-term disputes. (Full article...) -
Image 3

Extent of the Silk Road and Spice trade routes blocked by the Ottoman Empire in 1453 spurring exploration
The historical origins of globalization (also known as historical globalization) are the subject of ongoing debate. Though many scholars situate the origins of globalization in the modern era (around the 19th century), others regard it as a phenomenon with a long history, dating back thousands of years (a concept known as archaic globalization). The period in the history of globalization roughly spanning the years between 1600 and 1800 is in turn known as the proto-globalization. (Full article...) -
Image 4A multinational corporation (MNC; also called a multinational enterprise (MNE), transnational enterprise (TNE), transnational corporation (TNC), international corporation, or state less corporation) is a corporate organization that owns and controls the production of goods or services in at least one country other than its home country. Control is considered an important aspect of an MNC to distinguish it from international portfolio investment organizations, such as some international mutual funds that invest in corporations abroad solely to diversify financial risks.
Most of the current largest and most influential companies are publicly traded multinational corporations, including Forbes Global 2000 companies. (Full article...) -
Image 5

A world map on the Winkel tripel projection,
a low-error map projection adopted by the National Geographic Society for reference maps
A world map is a map of most or all of the surface of Earth. World maps, because of their scale, must deal with the problem of projection. Maps rendered in two dimensions by necessity distort the display of the three-dimensional surface of the Earth. While this is true of any map, these distortions reach extremes in a world map. Many techniques have been developed to present world maps that address diverse technical and aesthetic goals.
Charting a world map requires global knowledge of the Earth, its oceans, and its continents. From prehistory through the Middle Ages, creating an accurate world map would have been impossible because less than half of Earth's coastlines and only a small fraction of its continental interiors were known to any culture. With exploration that began during the European Renaissance, knowledge of the Earth's surface accumulated rapidly, such that most of the world's coastlines had been mapped, at least roughly, by the mid-1700s and the continental interiors by the twentieth century. (Full article...) -
Image 6

Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, convention centers (pictured here) were deemed to be ideal sites for temporary hospitals, due to their existing infrastructure (electrical, water, sewage). Hotels and dormitories were also considered appropriate because they can use negative pressure technology.
A pandemic (/pænˈdɛmɪk/ pan-DEM-ik) is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has a sudden increase in cases and spreads across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. Widespread endemic diseases with a stable number of infected individuals such as recurrences of seasonal influenza are generally excluded as they occur simultaneously in large regions of the globe rather than being spread worldwide.
Throughout human history, there have been a number of pandemics of diseases such as smallpox. The Black Death, caused by the Plague, caused the deaths of up to half of the population of Europe in the 14th century. The term pandemic had not been used then, but was used for later epidemics, including the 1918 H1N1 influenza A pandemic—more commonly known as the Spanish flu—which is the deadliest pandemic in history. The most recent pandemics include the HIV/AIDS pandemic, the 2009 swine flu pandemic and the COVID-19 pandemic. Almost all these diseases still circulate among humans though their impact now is often far less. (Full article...) -
Image 7

Path of the Centurion under the command of George Anson
While Great Britain was fighting the War of Jenkins' Ear with Spain in 1740, Commodore George Anson led a squadron of eight ships on a mission to disrupt or capture the Pacific Ocean possessions of the Spanish Empire. Returning to Britain in 1744 by way of China and thus completing a circumnavigation of the globe, the voyage was notable for the capture of the Manila galleon, but also for horrific losses from disease with only 188 men of the original 1,854 surviving. An account of the voyage was published in 1748 which being widely read by the general public was a great commercial success and "is still esteemed as the story of a remarkable voyage extremely well told." (Full article...)
General images - load new batch
-
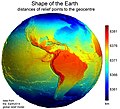
Image 1Earth's western hemisphere showing topography relative to Earth's center instead of to mean sea level, as in common topographic maps (from Earth)
-
Image 4Fall of the Berlin Wall, 1989
-
Image 5A pillar at Neolithic Göbekli Tepe
-
Image 6Shanghai. China urbanized rapidly in the 21st century.
-
Image 7A 580 million year old fossil of Spriggina floundensi, an animal from the Ediacaran period. Such life forms could have been ancestors to the many new forms that originated in the Cambrian Explosion. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 8The first airplane, the Wright Flyer, flew on 17 December 1903.
-
Image 9Chloroplasts in the cells of a moss (from History of Earth)
-
Image 11The pale orange dot, an artist's impression of the early Earth which might have appeared orange through its hazy methane rich prebiotic second atmosphere. Earth's atmosphere at this stage was somewhat comparable to today's atmosphere of Titan. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 13Change in average surface air temperature and drivers for that change. Human activity has caused increased temperatures, with natural forces adding some variability. (from Earth)
-
Image 14A computer-generated image mapping the prevalence of artificial satellites and space debris around Earth in geosynchronous and low Earth orbit (from Earth)
-
Image 15Lithified stromatolites on the shores of Lake Thetis, Western Australia. Archean stromatolites are the first direct fossil traces of life on Earth. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 16Tiktaalik, a fish with limb-like fins and a predecessor of tetrapods. Reconstruction from fossils about 375 million years old. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 18Pale orange dot, an artist's impression of Early Earth, featuring its tinted orange methane-rich early atmosphere (from Earth)
-
Image 19Graph showing range of estimated partial pressure of atmospheric oxygen through geologic time (from History of Earth)
-
Image 20Cuneiform inscription, eastern Turkey
-
Image 21One of the eleven Rock-hewn Churches of Lalibela constructed during the Zagwe dynasty in Ethiopia (from Human history)
-
Image 25Empires of the world in 1898
-
Image 26Standing Buddha from Gandhara, 2nd century CE
-
Image 29A composite image of Earth, with its different types of surface discernible: Earth's surface dominating Ocean (blue), Africa with lush (green) to dry (brown) land and Earth's polar ice in the form of Antarctic sea ice (grey) covering the Antarctic or Southern Ocean and the Antarctic ice sheet (white) covering Antarctica. (from Earth)
-
Image 30Earth's land use for human agriculture in 2019 (from Earth)
-
Image 31Successive dispersals of Homo erectus (yellow), Homo neanderthalensis (ochre) during Out of Africa I and Homo sapiens (red, Out of Africa II), with the numbers of years since they appeared before present. (from Human history)
-
Image 32Vitruvian Man by Leonardo da Vinci epitomizes the advances in art and science seen during the Renaissance. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 33A banded iron formation from the 3.15 Ga Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Red layers represent the times when oxygen was available; gray layers were formed in anoxic circumstances. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 34Notre-Dame de Paris, France
-
Image 35Great Pyramids of Giza, Egypt
-
Image 38Artist's impression of a Hadean landscape with the relatively newly formed Moon still looming closely over Earth and both bodies sustaining strong volcanism. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 39Geologic map of North America, color-coded by age. From most recent to oldest, age is indicated by yellow, green, blue, and red. The reds and pinks indicate rock from the Archean.
-
Image 40A view of Earth with different layers of its atmosphere visible: the troposphere with its clouds casting shadows, a band of stratospheric blue sky at the horizon, and a line of green airglow of the lower thermosphere around an altitude of 100 km, at the edge of space (from Earth)
-
Image 41A map of heat flow from Earth's interior to the surface of Earth's crust, mostly along the oceanic ridges (from Earth)
-
Image 42A reconstruction of Pannotia (550 Ma). (from History of Earth)
-
Image 43Yggdrasil, an attempt to reconstruct the Norse world tree which connects the heavens, the world, and the underworld. (from World)
-
Image 44Benin Bronze head from Nigeria
-
Image 45Artist's impression of the enormous collision that probably formed the Moon (from History of Earth)
-
Image 47An artist's impression of the Archean, the eon after Earth's formation, featuring round stromatolites, which are early oxygen-producing forms of life from billions of years ago. After the Late Heavy Bombardment, Earth's crust had cooled, its water-rich barren surface is marked by continents and volcanoes, with the Moon still orbiting Earth half as far as it is today, appearing 2.8 times larger and producing strong tides. (from Earth)
-
Image 48The replicator in virtually all known life is deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is far more complex than the original replicator and its replication systems are highly elaborate. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 49A 2012 artistic impression of the early Solar System's protoplanetary disk from which Earth and other Solar System bodies were formed (from Earth)
-
Image 50Artist's conception of Hadean Eon Earth, when it was much hotter and inhospitable to all forms of life. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 51Trilobites first appeared during the Cambrian period and were among the most widespread and diverse groups of Paleozoic organisms. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 52A view of Earth with its global ocean and cloud cover, which dominate Earth's surface and hydrosphere; at Earth's polar regions, its hydrosphere forms larger areas of ice cover. (from Earth)
-
Image 53Artist's impression of Earth during the later Archean, the largely cooled planetary crust and water-rich barren surface, marked by volcanoes and continents, features already round microbialites. The Moon, still orbiting Earth much closer than today and still dominating Earth's sky, produced strong tides. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 54Atomic bombing of Nagasaki, 1945
-
Image 56Earth's night-side upper atmosphere appearing from the bottom as bands of afterglow illuminating the troposphere in orange with silhouettes of clouds, and the stratosphere in white and blue. Next the mesosphere (pink area) extends to the orange and faintly green line of the lowest airglow, at about one hundred kilometers at the edge of space and the lower edge of the thermosphere (invisible). Continuing with green and red bands of aurorae stretching over several hundred kilometers. (from Earth)
-
Image 57An animation of the changing density of productive vegetation on land (low in brown; heavy in dark green) and phytoplankton at the ocean surface (low in purple; high in yellow) (from Earth)
-
Image 58Last Moon landing: Apollo 17 (1972)
-
Image 59Pangaea was a supercontinent that existed from about 300 to 180 Ma. The outlines of the modern continents and other landmasses are indicated on this map. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 62Obelisk of Axum, Ethiopia
-
Image 63Tracy Caldwell Dyson, a NASA astronaut, observing Earth from the Cupola module at the International Space Station on 11 September 2010 (from Earth)
-
Image 6813th-century French historiated initial with the three classes of medieval society: those who prayed (the clergy), those who fought (the knights), and those who worked (the peasantry)
-
Image 71Artist's rendition of an oxinated fully-frozen Snowball Earth with no remaining liquid surface water. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 73Angkor Wat temple complex, Cambodia, early 12th century
-
Image 74Earth's axial tilt causing different angles of seasonal illumination at different orbital positions around the Sun (from Earth)
-
Image 75Earth's history with time-spans of the eons to scale. Ma means "million years ago". (from History of Earth)
-
Image 76Dinosaurs were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates throughout most of the Mesozoic (from History of Earth)
-
Image 77Olmec colossal head, now at the Museo de Antropología de Xalapa
-
Image 78A schematic view of Earth's magnetosphere with solar wind flowing from left to right (from Earth)
-
Image 80An artist's impression of ice age Earth at glacial maximum. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 83Battle during the 1281 Mongol invasion of Japan
-
Image 84Portrait of Alfraganus in the Compilatio astronomica, 1493. Islamic astronomers began just before the 9th century to collect and translate Indian, Persian and Greek astronomical texts, adding their own astronomy and enabling later, particularly European astronomy to build on. Symbolic for the post-classical period, a period of an increasing trans-regional literary culture, particularly in the sciences, spreading and building on methods of science. (from Human history)
-
Image 85A reconstruction of human history based on fossil data. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 87Japanese depiction of a Portuguese carrack, a result of globalizing maritime trade
Megacities of the world - show another
Kinshasa (/kɪnˈʃɑːsə/; French: [kinʃasa]; Lingala: Kinsásá), formerly named Léopoldville from 1881–1966 (Dutch: Leopoldstad), is the capital and largest city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Kinshasa is one of the world's fastest-growing megacities, with an estimated population of 17 million in 2024. It is the most densely populated city in the DRC, the most populous city and third-largest metropolitan area in Africa, and the world's twenty-second most populous city and fourth-most populous capital city. It is the leading economic, political, and cultural center of the DRC, housing several industries including manufacturing, telecommunications, banking, and entertainment. The city also hosts some of DRC's significant institutional buildings, such as the People's Palace, Palace of the Nation, Court of Cassation, Constitutional Court, African Union City, Marble Palace, Martyrs Stadium, Government House, Kinshasa Financial Center, and other national departments and agencies.
The Kinshasa site has been inhabited by Bantus (Teke, Humbu [fr]) for centuries and was known as Nshasa before transforming into a commercial hub during the 19th and 20th centuries. The city was named Léopoldville by Henry Morton Stanley in honor of Leopold II of Belgium. The name was changed to Kinshasa in 1966 during Mobutu Sese Seko's Zairianisation campaign as a tribute to Nshasa village. Covering 9,965 square kilometers, Kinshasa stretches along the southern shores of the Pool Malebo on the Congo River. It forms an expansive crescent across flat, low-lying terrain at an average altitude of about 300 meters. Kinshasa borders the Mai-Ndombe Province, Kwilu Province, and Kwango Province to the east; the Congo River delineates its western and northern perimeters, constituting a natural border with the Republic of the Congo; to the south lies the Kongo Central Province. Across the river sits Brazzaville, the smaller capital of the neighboring Republic of the Congo, forming the world's second-closest pair of capital cities despite being separated by a four-kilometer-wide unbridged span of the Congo River. (Full article...)
Did you know - load new batch

- ... that a modern Polish fairy tale, written during the period of martial law in Poland in the 1980s, mixes the themes of real-world environmental protection and fantasy-like gnomes?
- ... that the zookeeper of the "loneliest elephant in the world" credited her with saving his marriage?
- ... that Aucklanders have a reputation for making false earthquake reports on New Zealand's earthquake monitoring website GeoNet?
- ... that at the age of 19, Van E. Chandler was the youngest pilot in the United States Armed Forces to become a flying ace during World War II?
- ... that homes in urban areas must have earthquake insurance before being connected to electricity in Turkey?
- ... that Carol Wilson had to pretend that she was a schoolteacher when unofficially representing England at the 1971 Women's World Cup?
- ... that the developers of Sonic felt the series' linear design contained "little room for evolution" so they decided to make Sonic Frontiers an open world game?
- ... that the Central Powers brought their armies under a supreme headquarters in September 1916, 18 months before the Allies did the same?
Countries of the world - show another

Paraguay, officially the Republic of Paraguay, is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to the east and northeast, and Bolivia to the northwest. It has a population of around 6.1 million, nearly 2.3 million of whom live in the capital and largest city of Asunción, and its surrounding metro area.
Spanish conquistadores arrived in 1524, and in 1537 established the city of Asunción, the first capital of the Governorate of the Río de la Plata. During the 17th century, Paraguay was the center of Jesuit missions, where the native Guaraní people were converted to Christianity and introduced to European culture. After the expulsion of the Jesuits from Spanish territories in 1767, Paraguay increasingly became a peripheral colony. Following independence from Spain in the early 19th century, Paraguay was ruled by a series of authoritarian governments. This period ended with the disastrous Paraguayan War (1864–1870), during which the country lost half its prewar population and around 25–33% of its territory. In the 20th century, Paraguay faced another major international conflict—the Chaco War (1932–1935) against Bolivia—in which Paraguay prevailed. The country came under a succession of military dictators, culminating in the 35-year regime of Alfredo Stroessner, which lasted until his overthrow in 1989 by an internal military coup. This marked the beginning of Paraguay's current democratic era. (Full article...)
The Seven Wonders of Poland (Polish: Siedem cudów Polski) is a short list of cultural wonders located in Poland. The creation of the list was initiated by the leading Polish newspaper Rzeczpospolita in a country-wide plebiscite held in September 2007. The results were published in the following month. (Full article...)
Related portals
Protected areas of the world - load new batch
-
Image 1

The northernmost tip of Prins Karls Forland in Forlandet National Park
Svalbard is an Arctic wilderness archipelago comprising the northernmost part of Norway. There are twenty-nine protected natural areas, consisting of seven national parks, six nature reserves, fifteen bird sanctuaries and one geotope protected area. In addition, human traces dating from before 1946 are automatically protected. The protected areas make up 39,800 square kilometers (15,400 sq mi) or 65% of the land area, and 78,000 square kilometers (30,000 sq mi) or 86.5% of the territorial waters. The largest protected areas are Nordaust-Svalbard Nature Reserve and Søraust-Svalbard Nature Reserve, which cover most of the areas east of the main island of Spitsbergen, including the islands of Nordaustlandet, Edgeøya, Barentsøya, Kong Karls Land and Kvitøya. Six of the national parks are located on Spitsbergen. Ten of the bird sanctuaries and the Moffen Nature Reserve are located within national parks. Five of the bird sanctuaries are Ramsar sites and fourteen of the bird sanctuaries are islands. Svalbard is on Norway's tentative list for nomination as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
The supreme responsibility for conservation lies with the Norwegian Ministry of the Environment, which has delegated the management to the Governor of Svalbard and the Norwegian Directorate for Nature Management. The foundation for conservation was established in the Svalbard Treaty of 1920, and has been further specified in the Svalbard Environmental Act of 2001. The first round of protection took force on 1 July 1973, when most of the current protected areas came into effect. This included the two large nature reserves and three of the national parks. Moffen Nature Reserve was established in 1983, followed by four national parks, three nature reserves and one geotope protection area between 2002 and 2005. (Full article...) -
Image 2Protected areas of Turkmenistan include nine nature reserves (zapovednik) and 13 sanctuaries (zakaznik) with a total area of 19,750 km2 or more than 4% of Turkmenistan's territory. (Full article...)
-
Image 3Protected areas of Norway include:
About 17 percent of the mainland of Norway is protected. Of this, ca. 8.3 percent is national parks, 1.3 percent is nature reserves and 4.7 percent otherwise protected. (Full article...) -
Image 4The protected areas of Finland include national parks, nature reserves and other areas, with a purpose of conserving areas of all of Finland's ecosystems and biotopes.
Protected areas include:- National parks of Finland (Kansallispuisto/Nationalpark) – 8,170 km2
- Strict nature reserves of Finland (Luonnonpuisto/Naturreservat) – 1,530 km2
- Mire reserves of Finland (Soidensuojelualue/Myrskyddsområde) – 4,490 km2
- Protected herb-rich forest areas (Lehtojensuojelualue/Lundskyddsområde) – 13 km2
- Protected old-growth forest areas (Vanhat metsät/Gamla skogar) – 100 km2
- Grey seal protection areas (Hylkeidensuojelualue/Sälskyddsområde) – 190 km2
- Other protected areas on state-owned land – 468 km2
-
Image 5

Ludaš Lake is a shallow lake in the province of Vojvodina in northern Serbia, near the city of Subotica. It is a special natural preserve and, since 1977, designated as a swamp area of international significance by the Ramsar Convention.
Protected areas cover around 5% of the territory of Serbia. The Law on the Protection of the Nature defines these categories of protected areas:- Strict nature reserve — Area of unmodified natural features with representative ecosystems set aside for the preservation of its biodiversity and for scientific research and monitoring.
- Special nature reserve — Area of unmodified or slightly modified natural features of great importance due to uniqueness and rarity which includes the habitats of endangered species set aside for the preservation of its unique features, education, limited tourism and for scientific research and monitoring.
- National park — Area with large number of diverse ecosystems of national value, with outstanding natural features and/or cultural heritage set aside for the preservation of its natural resources and for educational, scientific and tourist use.
- Natural monument — Small unmodified or slightly modified natural feature, object or phenomenon, easily detectable and unique, with unique natural attributes.
- Protected habitat — Area which includes habitats of one or more wildlife species.
- Landscape of outstanding features — Area of remarkable appearance with important natural and cultural value.
- Nature park — Area of well-preserved natural values with preserved natural ecosystems and picturesque landscape set aside for the preservation of biodiversity and for educational, tourist, recreational and scientific use.
-
Image 6

West Matukituki Valley and the Matukituki River seen from Cascade Saddle in Mount Aspiring National Park
Protected areas of New Zealand are areas that are in some way protected to preserve their environmental, scientific, scenic, historical, cultural or recreational value. There are about 10,000 protected areas, covering about a third of the country. The method and aims of protection vary according to the importance of the resource and whether it is publicly or privately owned.
Nearly 30 percent of New Zealand's land mass is publicly owned with some degree of protection. Most of this land – about 80,000 square kilometres (31,000 sq mi) – is administered by the Department of Conservation. There are 13 national parks, thousands of reserves, 54 conservation parks, and a range of other conservation areas. (Full article...) -
Image 7
Heathland at the Hoge Kempen National Park
There are numerous protected areas in Belgium with a wide variety of types, protection levels and sizes. The below list gives an overview of the most important protected areas. (Full article...) -
Image 8Bihar is a state in East India. It is bounded by Uttar Pradesh to the west, Nepal to the north, West Bengal to the east and Jharkhand to the south. About 7% of the state is protected forest area. (Full article...)
-
Image 9
-
Image 10The state of Johor in Malaysia is noted for its national parks and forest reserves which preserve virgin rainforests known for its biodiversity and endangered species of animals.
Mangrove swamps and coral reefs are also protected within these parks. (Full article...) -
Image 11This is a list of protected areas in Botswana. (Full article...)
-
Image 12
-
Image 13A list of protected areas of Oman:
- Al Jabal Algharbi Nature Reserve
- Aldhahra Nature Reserve
- Alburaimi Oasis Nature Reserve
- Oryx Nature Reserve
- Turtle Reserve
- Ad Dimaniyat Islands Reserve
- Al Saleel National Park (As Salil Natural Park)
- Jabal Samhan Nature Reserve
- Al Jabal Al Akhdar Scenic Reserve
- Western Hajer Stars Lights Reserve
- Al Rustaq Wildlife Reserve
- Al Wusta Wetland Reserve
- Jabal Qahwan Nature Reserve
- Al Sareen Nature Reserve
- Ras al Shajar Nature Reserve
- Al Khuwuair Nature Reserve
- Khawrs of the Dhofar Coast Reserve
-
Image 14The Protected areas of Portugal (Portuguese: Áreas protegidas de Portugal) are classified under a legal protection statute that allows for the adequate protection and maintenance of biodiversity, while providing services for ecosystem that maintains the natural and geological patrimony. (Full article...)
-
Image 15

The Valley of the Giants skywalk at Walpole-Nornalup National Park
Western Australia is the second largest country subdivision in the world.
As of 2022, based on the latest Collaborative Australian Protected Areas Database report, it contains 1857 separate land-based protected areas with a total area of 76,142,710 hectares (188,152,700 acres), accounting for just over 30 percent of the state's land mass. By area, Indigenous Protected Areas account for the largest part of this, almost 67 percent while, by number, nature reserves hold the majority with two-third of all land-based protected areas being nature reserves. (Full article...)
Selected world maps
-
Image 1Index map from the International Map of the World (1:1,000,000 scale)
-
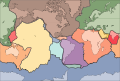
Image 2A plate tectonics map with volcano locations indicated with red circles
-
Image 3Time zones of the world
-
Image 4Only a few of the largest large igneous provinces appear (coloured dark purple) on this geological map, which depicts crustal geologic provinces as seen in seismic refraction data
-
Image 5Mollweide projection of the world
-
Image 6United Nations Human Development Index map by country (2016)
-
Image 7The Goode homolosine projection is a pseudocylindrical, equal-area, composite map projection used for world maps.
-
Image 8The world map by Gerardus Mercator (1569), the first map in the well-known Mercator projection
-
Image 91516 map of the world by Martin Waldseemüller
World records
- List of Olympic records in athletics
- List of world records in athletics
- List of junior world records in athletics
- List of world records in masters athletics
- List of world youth bests in athletics
- List of IPC world records in athletics
- List of world records in canoeing
- List of world records in chess
- List of cycling records
- List of world records in track cycling
- List of world records in finswimming
- List of world records in juggling
- List of world records in rowing
- List of world records in speed skating
- List of world records in swimming
- List of IPC world records in swimming
- List of world records in Olympic weightlifting
Topics
Continents of Earth | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Cenozoic Era (present–66.0 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesozoic Era (66.0–252 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
| Paleozoic Era (252–539 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
| Proterozoic Eon (539 Ma–2.5 Ga) |
| ||||||||||||
| Archean Eon (2.5–4 Ga) | |||||||||||||
| Hadean Eon (4–4.6 Ga) | |||||||||||||
ka = kiloannum (thousand years ago); Ma = megaannum (million years ago); Ga = gigaannum (billion years ago). See also: Geologic time scale • | |||||||||||||
| City proper | |
|---|---|
| Metropolitan area | |
| Urban area/agglomeration | |
| Historical | |
| Related articles | |
| Locations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Related | ||
| Retrospectively recognized expositions | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIE-recognized Universal expositions | |||||||||||||
| BIE-recognized specialized expositions |
| ||||||||||||
| BIE-recognized horticultural exhibitions (AIPH) | |||||||||||||
| Not BIE- recognized |
| ||||||||||||
†Postponed to 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic | |||||||||||||
| Confederations | |
|---|---|
| World Championships | |
| World Cup | |
| Special events | |
| Presidents |
|
| Awards | |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Economic classification of countries | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three-World Model | |||||
| Gross domestic product (GDP) |
| ||||
| Gross national income (GNI) | |||||
| Wages | |||||
| Wealth | |||||
| Other national accounts | |||||
| Human development | |||||
| Digital divide | |||||
| Net international investment position (NIIP) | |||||
| Technological |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociological | |||||
| Ecological |
| ||||
| Biological |
| ||||
| Astronomical | |||||
| Eschatological |
| ||||
| Others |
| ||||
| Fictional | |||||
| Organizations | |||||
| Theatres |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Principal participants |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Timeline |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Aspects |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| General |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Timeline |
| ||||||||||||||||
Categories
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikispecies
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus